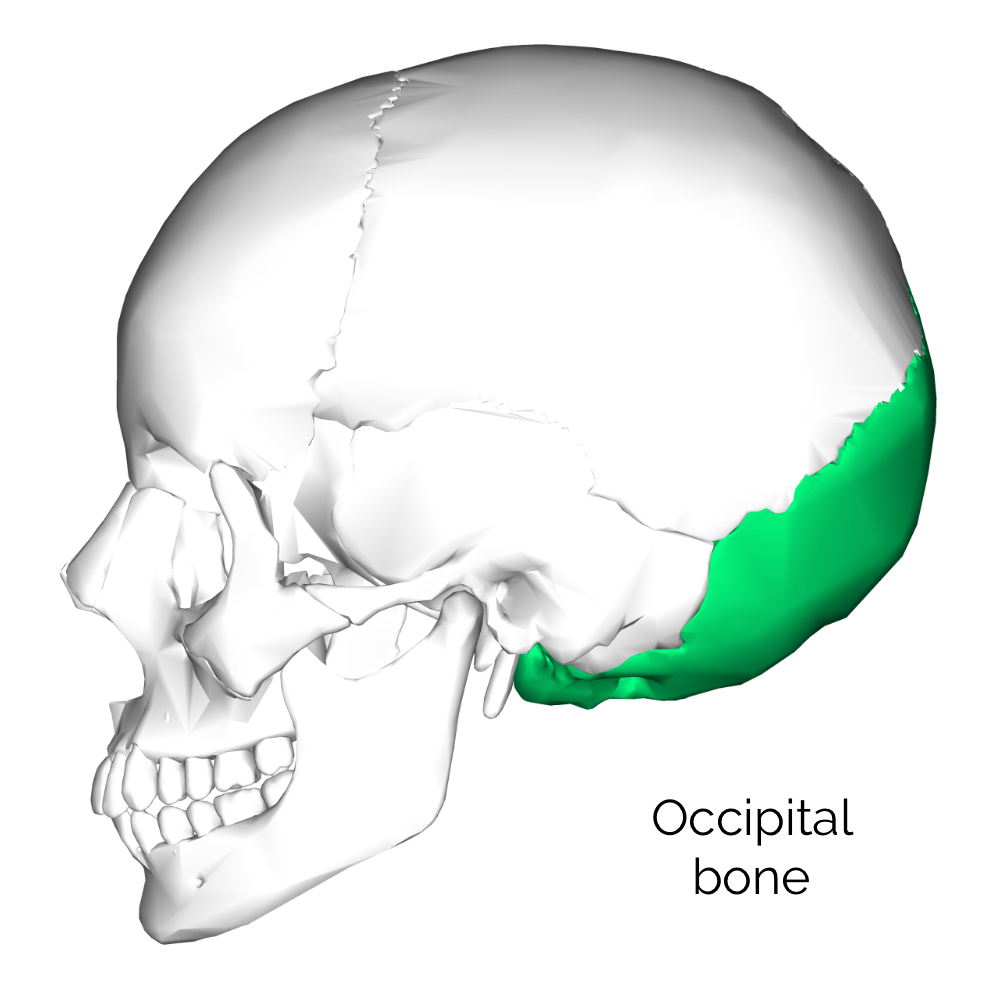
The occipital bone is the trapezoidshaped bone at the lowerback of the cranium (skull) The occipital bone houses the back part of the brain and is one of seven bones that come together to form the skull It is located next to five of the cranium bones An anatomy lesson is a good place to start This article will help you understand key anatomical structures in the skull and spine, with the goal of helping you better understand your condition The Craniovertebral Junction Where Your Head and Neck MeetEpidural hematoma Bleeding between the tough tissue (dura) lining the inside of the skull and the skull itself, usually shortly after a head injury Initial mild symptoms can progress rapidly to

Skull Scalp And Superficial Face
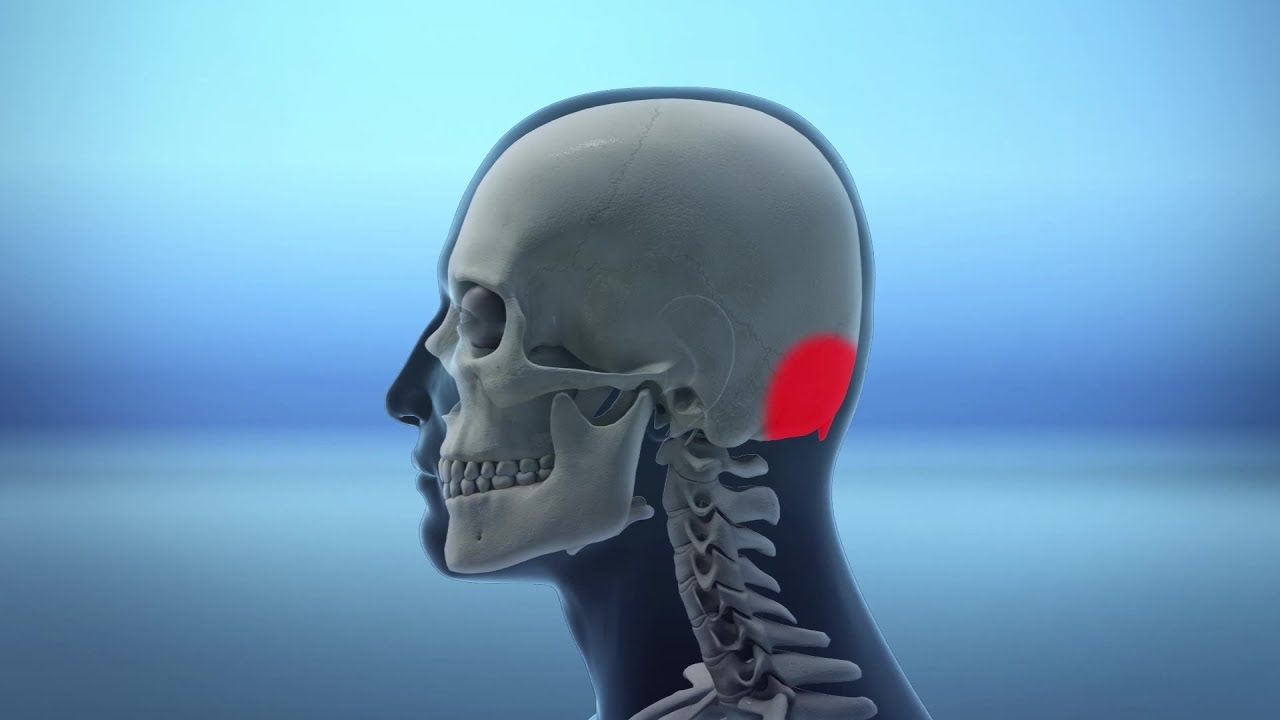
Sore head at back of skull
Sore head at back of skull-In medical term, it is called as Occipital neuralgia It is a condition in which the nerves that go from the top of the spinal cord up via the scalp, named the occipital nerves, are swollen or injured And you might feel pain in back of your head at base of your skull and Nausea 13,276 anatomy of the head and neck stock photos, vectors, and illustrations are available royaltyfree See anatomy of the head and neck stock video clips of 133 muscle head anatomy vocal organ diagram female neck anatomy neck wireframe head neck human anatomy head artery anatomy face pharynx vector neck degree head anatomy 3d



3
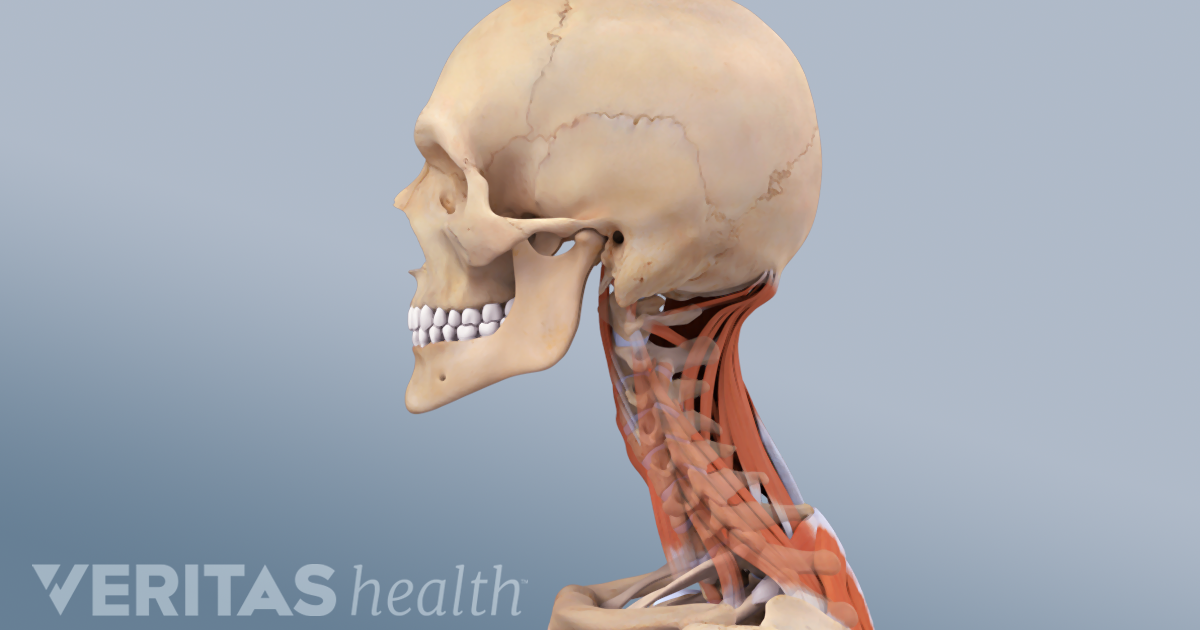
The cranial base, also known as the base of the skull or skull ba s e, is the most inferior part of the skull forming the floor of the cranial cavity The cranial base is formed by six different bones the ethmoid, sphenoid, occipital, frontal, paired parietal and temporal bonesBack of head, back part of the head or skull (Anatomy) occiput () Flemish Anatomist who made discoveries about Human Anatomy which surpassed those Near the base of the skull are a group of muscles called the suboccipital muscles There are 4 paired muscles that attach to the upper two cervical bones (1) The suboccipital muscles can become tense and tender due to factors such as eye strain, wearing new eyeglasses, poor ergonomics at a computer workstation, poor posture, and trauma
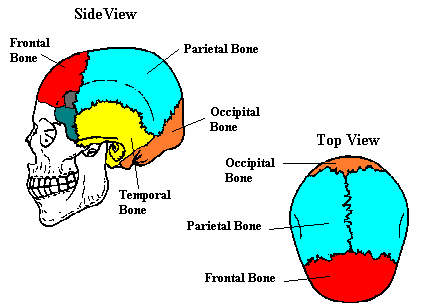
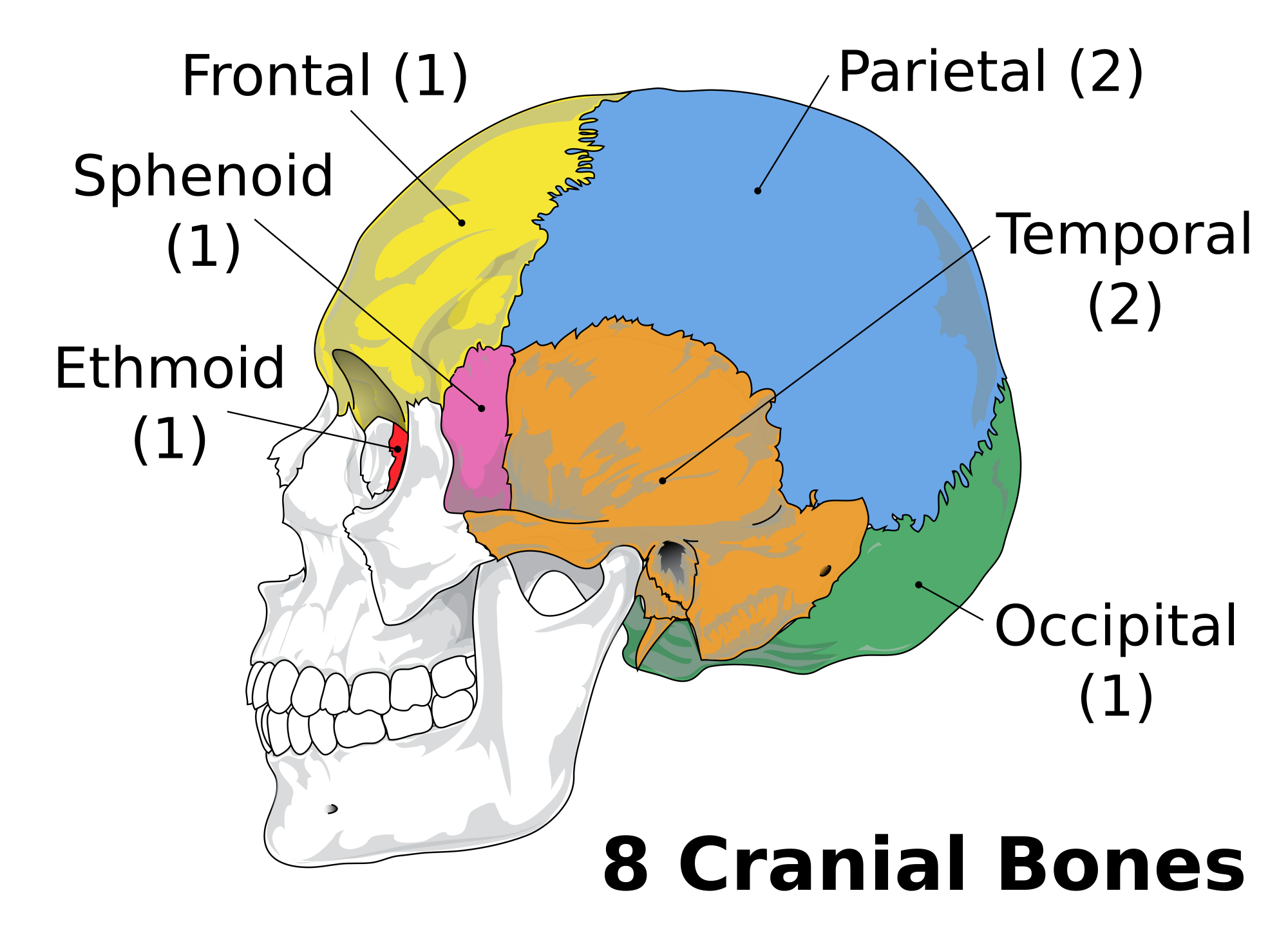
1 Occipital Condyles where the skull articulates with the first cervical vertebrae 2 foramen magnum is also seen, which is where the spinal cord leaves the skull 3 sphenoid sinus This sinus drains via the aperture of the sphenoid sinus (top of body on both sides anteriorly) 4 The spine is the backbone of the human skeleton Anatomy is the science that studies the structure of the body The shoulder is designed to be incredibly flexible, enabling a wide range of motion The muscles of the neck run from the base of the skull to the upper back and work together to bend the head and assist in breathingHuman skeleton, skull front and back The human skull is generally considered to consist of twentytwo bones %u14 eight cranial bones and fourteen facial skeleton bones In the neurocranium these are the occipital bone, two temporal bones, two parietal bones, the sphenoid, ethmoid and frontal bones
The Organs of the Head include the ear, the eye, the nose and sinuses, the salivary glands, and the oral cavity The ear can be divided in to three sections the external ear, the middle ear, and the inner earThe external ear functions to capture and direct sound waves through the external acoustic meatus to reach the tympanic membrane (ear drum) ) The tympanic membrane marksAbout Skull Anatomy Skull reshaping is done on any of the structures that lie above the face The simplest way to make the difference between the head and the face is to envision a ring that wraps around the head at the level of the eyes Anything above is the head or skull and what lies below is the face This can also be called the The spine is the backbone of the human skeleton Together, the bones of the skull support the structure of the face and shelter the brain and brain stem The spine provides support to hold the head and body up straight Learn how the housefly uses its anatomy to survive and why housefly meals arrive through a plunger



3
:background_color(FFFFFF):format(jpeg)/images/library/9490/skull-posterior-lateral-views_english.jpg)



Posterior And Lateral Views Of The Skull Anatomy Kenhub
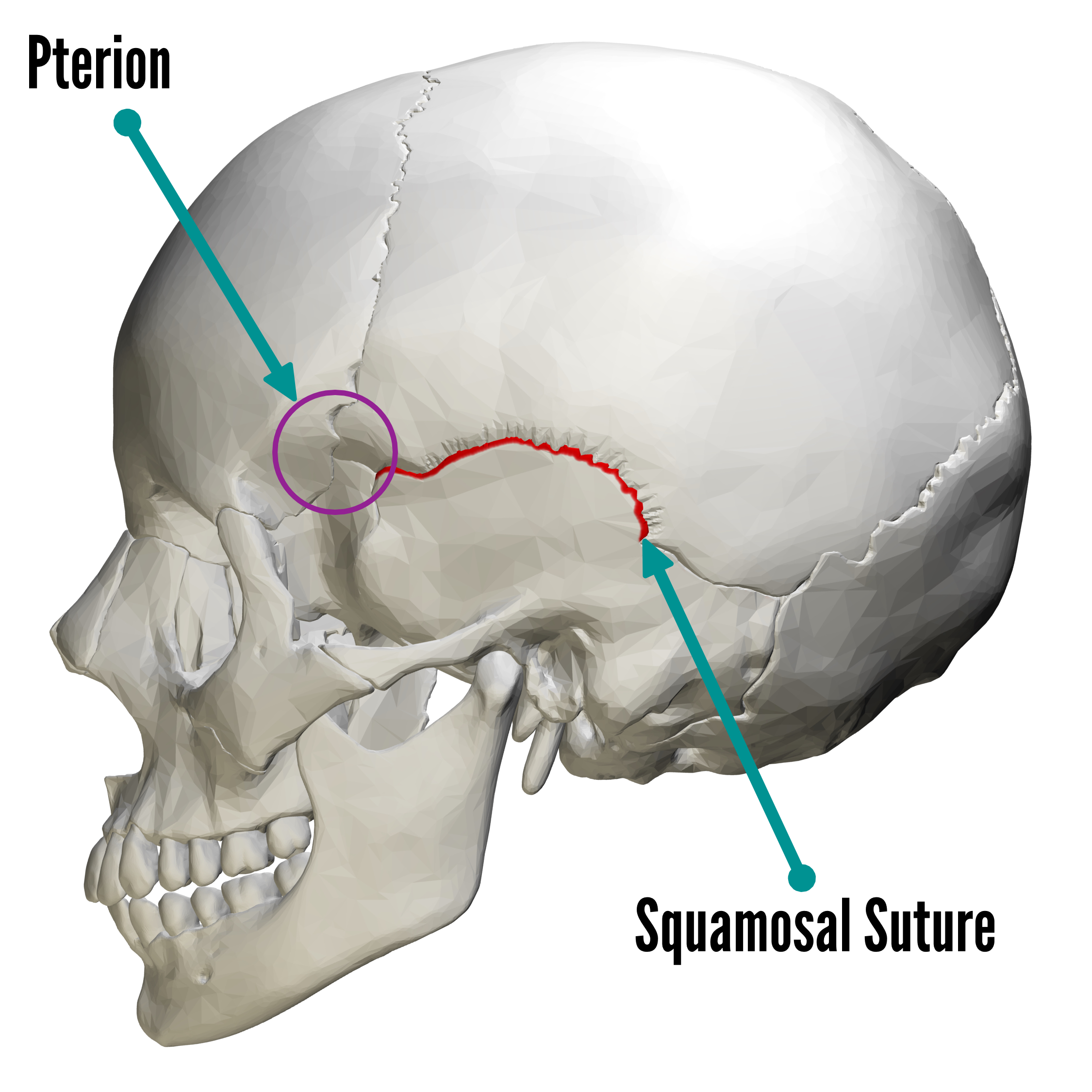
The head is comprised of many bones that form a shelllike bony structure that protects the brain the skull While the bony framework of the neck is define They move the head in every direction, pulling the skull and jaw towards the shoulders, spine, and scapula Working in pairs on the left and right sides of the body, these muscles control the flexion and extension of the head and neck Working individually, these muscles rotate the head or flex the neck laterally to the left or right 10 / 10 ( 1 vote ) External Anatomy Of The Right Side Of The Skull In this image, you will find coronal suture, frontal bone, parietal bone, sphenoid bone, greater wing, squamous suture, lambdoid suture in it You may also find an occipital bone, temporal bone, ethmoid bone, lacrimal bone, lacrimal fossa, zygomatic process, nasal bone




Occipital Bun Wikipedia
/male-skull-in-profile-with-transparent-head-on-white-background-1092338382-d031fe3a88fa4462b0ba082a1ec64302.jpg)



Occipital Bone Anatomy Function And Treatment
Skull anatomy Frontal Bone Parietal Bone Sagital Suture Coronal Suture the large cranial bone forming the front part of the cranium either of two skull bones between the frontal and occipital bo Located on the midline of the skull lies between both parietal the suture between the parietal and frontal bones of the skull The orbicularis oris is a circular muscle that moves the lips, and the orbicularis oculi is a circular muscle that closes the eye The occipitofrontalis muscle moves up the scalp and eyebrows The muscle has a frontal belly and an occipital (near the occipital bone on the posterior part of the skull) belly In other words, there is a muscle on the forehead (frontalis) and one onThe Crown begins at the point where the top of the head begins to curve downward to the back of the head and ends at the point just above the Occipital bone It is a semicircular area Occipital BoneThe Occipital Bone is the small bony protrusion at



Why Do I Have A Bone Bump On The Back Of My Skull Quora
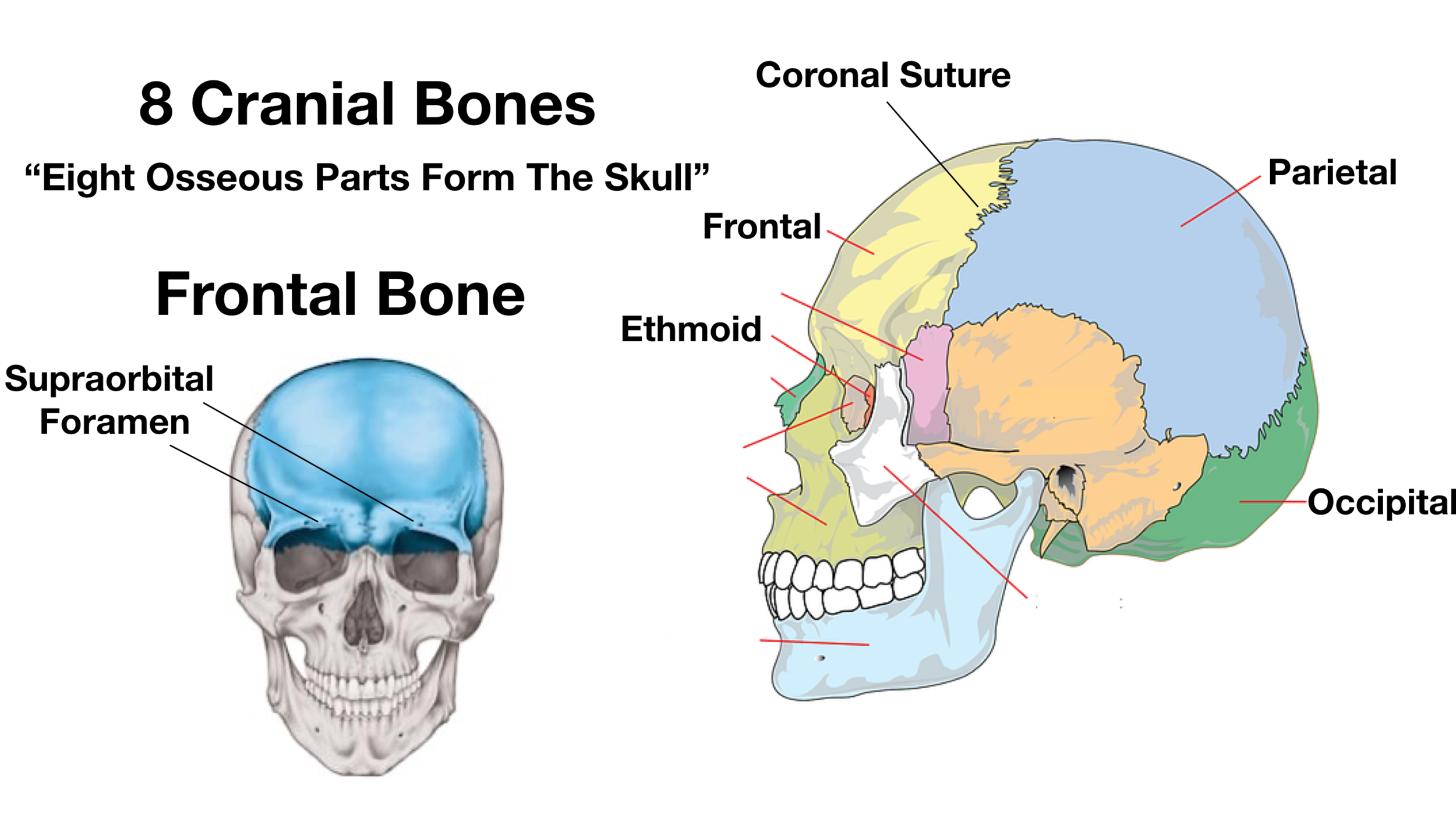



Skull Anatomy Cranial Bone And Suture Labeled Diagram Names Mnemonic Ezmed
Translation for 'back part of the skull which protrudes outward (Anatomy), bony projection on the back of the head' in English>English dictionary Search over 14 million words and phrases in more than 490 language pairs It is a complex anatomical structure weighing up to five kilograms that rests on the bony skull and in turn, the neck In addition to the evident ears, eyes, nose, and mouth, the head supports a variety of other important structures Muscles of mastication Facial musclesThe orbicularis oris is a circular muscle that moves the lips, and the orbicularis oculi is a circular muscle that closes the eye The occipitofrontalis muscle moves up the scalp and eyebrows The muscle has a frontal belly and an occipital (near the occipital bone on the posterior part of the skull) belly In other words, there is a muscle on the forehead (frontalis) and one on the back of




A P Lab Bones Skull Anatomy Flashcards Quizlet
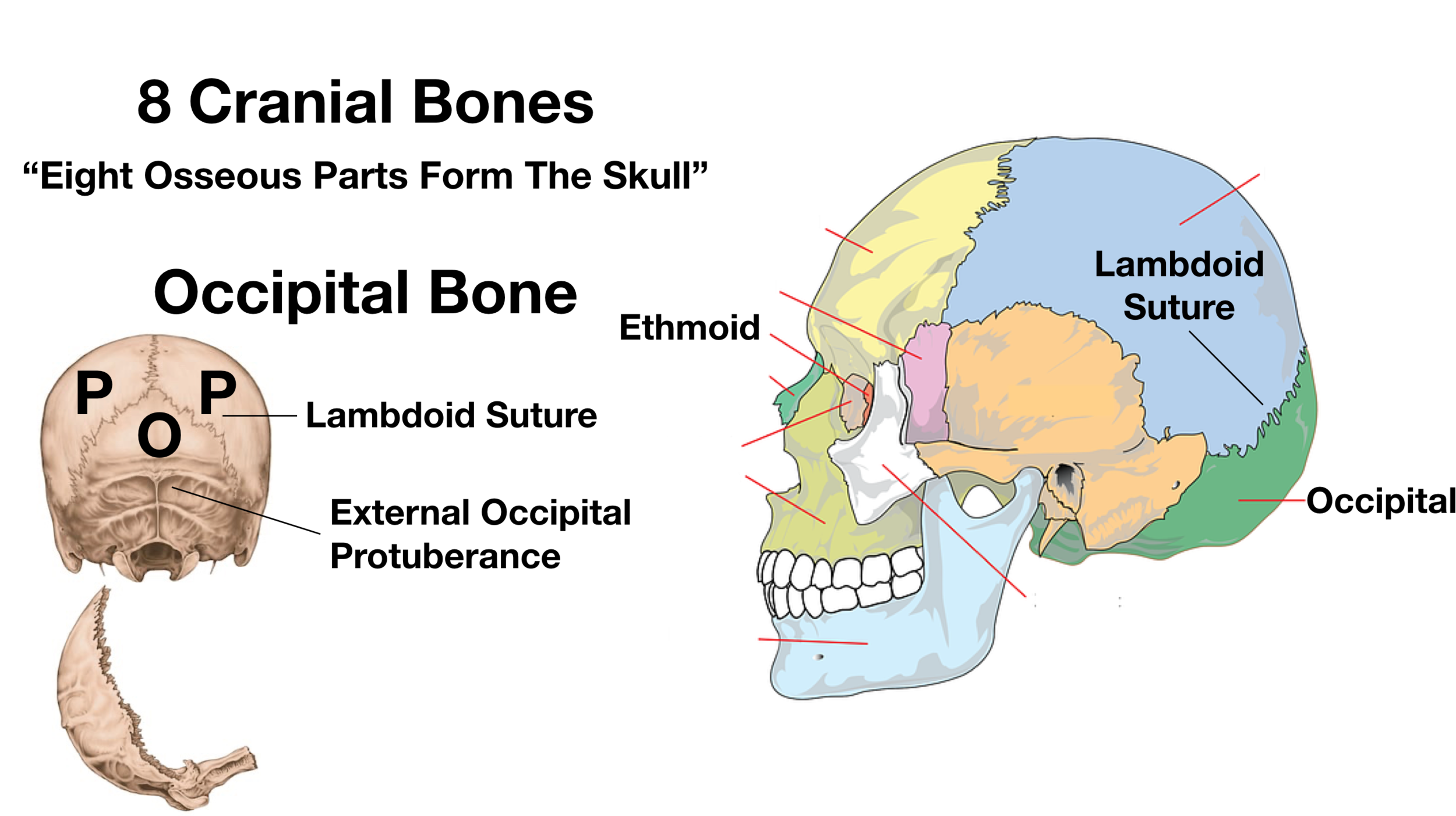



Skull Anatomy Cranial Bone And Suture Labeled Diagram Names Mnemonic Ezmed
Flat Back of the Head One of the most common aesthetic deformities of the entire skull is the flat back of the head Well known to occur from sleeping positions in infants and predisposed to occur in certain ethnic groups, lack of a nice shape to the back of Routine non–contrast material–enhanced head CT is one of the most frequently ordered studies in the emergency department Skull base–related pathologic entities, often depicted on the first or last images of a routine head CT study, can be easily overlooked in the emergency setting if not incorporated in the interpreting radiologist's search pattern, as the3D interactive models and tutorials on the anatomy of the head and face, including the musculature, osseus strutures, ear, orbit, nasal cavity and more!




Human Head Skull And Cervical Vertebrae Rear View Stock Photo Download Image Now Istock




Bones Of The Head And Neck Skull And Cervical Spine Preview Human Anatomy Kenhub Youtube
What is the Pain in Back of Head at Base of Skull ?The facial bones (14 bones 2zygomatic, 2maxillary, 2palatine, 2nasal, 2lacrimal, vomer, 2inferior conchae, mandible) The occipital bone joins with the atlas near the foramen magnum, a large hole ( foramen) at the base of the skull The atlas joinsThis is the second video about the skull anatomy and the bones of the head https//wwwAnimatedAnatomycom/ Click To Buy Our Anatomical Software And L
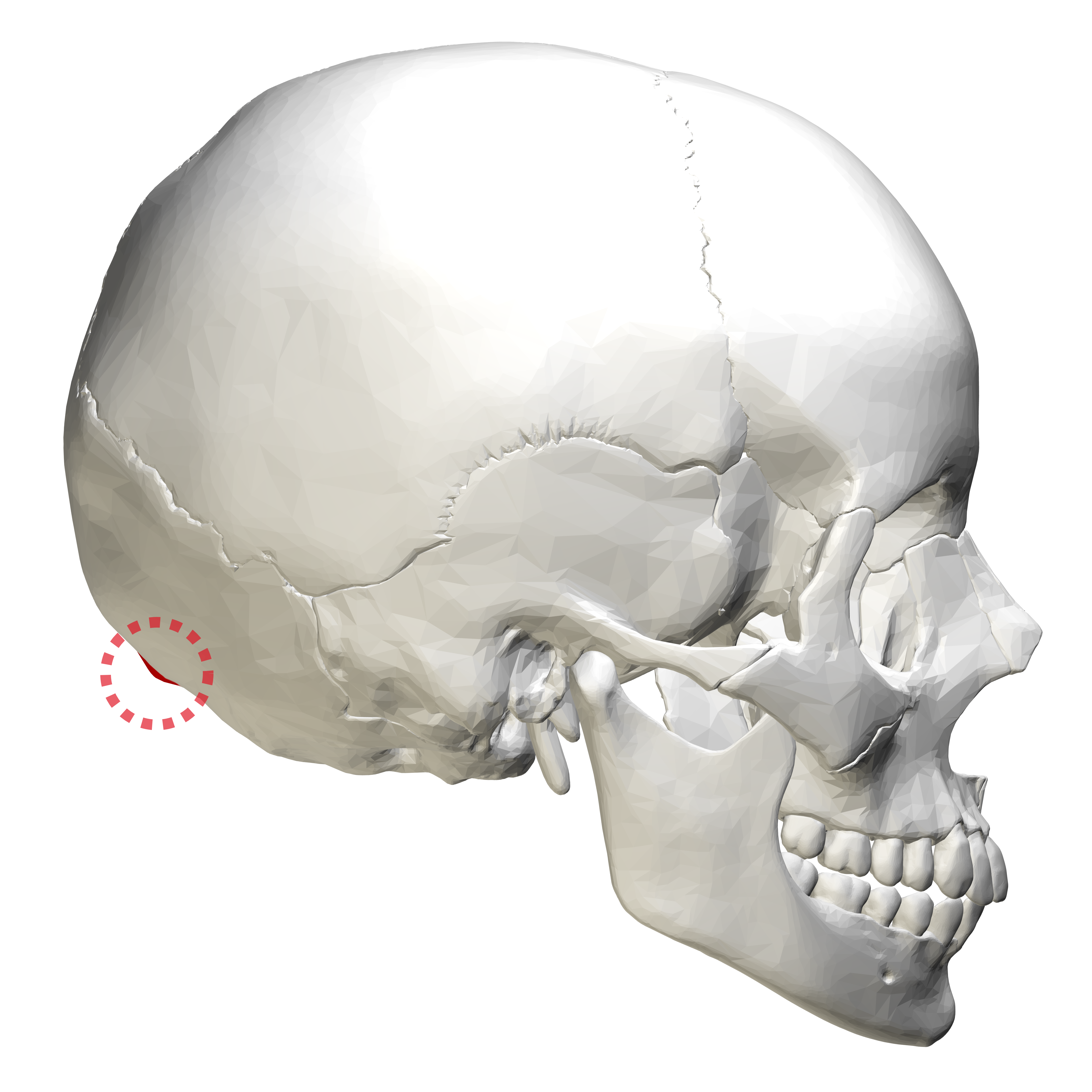



External Occipital Protuberance Wikipedia




Skull Anatomy Terminology Dr Barry L Eppley
Axial muscles of the head, neck, and back It offers protection to the brain, eye balls, inner ears, and nasal passages The skull includes the upper jaw and the cranium It supports and protects the face and the brain In order to be light, the skull is made up by flat and irregular bones, and has hollow spaces called the sinuses Learn moreBrowse 4,815 head and neck anatomy stock photos and images available, or search for head and neck cancer or squamous cell carcinoma to find more great stock photos and pictures Houman body parts flat line icons set Man, woman head, brain nose, mouth, foot, ear, lips vector illustration The nerves of the head and neck include the most vital and important organs of the nervous system — the brain and spinal cord — as well as the organs of the special senses In addition, in this region we also find the major cranial and spinal nerves that connect the central nervous system to the organs, skin, and muscles of the head and neck




Massage For Neck Pain Headaches Suboccipitals
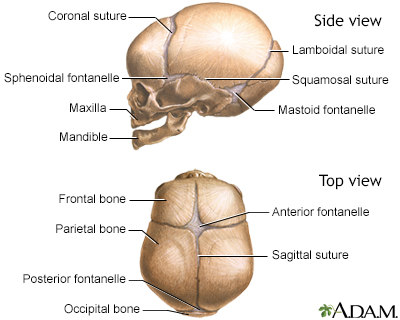



Cranial Sutures Information Mount Sinai New York
The cranium (also known as the neurocranium) is formed by the superior aspect of the skull It encloses and protects the brain, meninges, and cerebral vasculature Anatomically, the cranium can be subdivided into a roof and a base Cranial roof – comprised of the frontal, occipital and two parietal bonesUseful xray images head and neck anatomy stock pictures, royaltyfree photos & images black human anatomy icons head and neck anatomy stock illustrations anatomy, veins of face and neck, sinuses dura mater, diploe, victorian anatomical drawing 19th century head and neck anatomy stock illustrationsBack of skull Anatomy Overview, Anterior Skull Base, Middle Skull Base The greater portion of the anterior floor is convex and grooved by the frontal lobe gyri This portion of the skull base consists of the orbital portion of the frontal bone The ethmoid bone forms the central part of the floor, which is the deepest area of




Female Head Muscles Anatomy Back View Stock Illustration



The Skull Boundless Anatomy And Physiology
The spine provides support to hold the head and body up straight Explore how exactly your eyes help you see the world around you Anatomy is the identification and description of the structures of living things Upper Back Anatomy Sutures of the skull Anatomy Kenhub On this page, you'll find links to descriptions and pictures of the The skull base forms the floor of the cranial cavity and separates the brain from other facial structures This anatomic region is complex and poses surgical challenges for otolaryngologists and neurosurgeons alike Working knowledge of the normal and variant anatomy of the skull base is essential for effective surgical treatment of disease in this area There are a wide variety of causes of these bumps In addition, each human skull has a natural bump on the back of the head This bump,



Bones Of The Skull Skull Osteology Anatomy Geeky Medics




Skull Scalp And Superficial Face
The skull base forms the floor of the cranial cavity and separates the brain from other facial structures From an anatomical perspective, the skull is divided into two parts Inferior view of base of the skull Axial muscles of the head, neck, and back Learn skull anatomy with skull bones quizzes and diagram labeling exercises 115,084 human skull anatomy stock photos, vectors, and illustrations are available royaltyfree See human skull anatomy stock video clips of 1,151 skull system anatomy of skull anatomy skull skull lateral view skull anatomy occipital medical skeleton named facial bone anatomy mandible maxilla human anatomy lateral skull anatomy



Neuroscience For Kids The Skull




Anatomy Anatomy Massage Therapy Migraine



Skull Pictures Anatomy Diagram Body Maps



Side Back Human Skull Stock Illustrations 164 Side Back Human Skull Stock Illustrations Vectors Clipart Dreamstime




Occipital Surgery For Flat Spots On Head Dr Barry L Eppley




Flashcards Bones Axial Skeleton Skull Cavities Skull Anatomy Anatomy Bones Medical Anatomy




Anatomy Back Of Skull 2 Diagram Quizlet




Bone Structure Of The Face An Overview Of Dental Anatomy Continuing Education Course Dentalcare Com




Skull Anatomy Terminology Dr Barry L Eppley
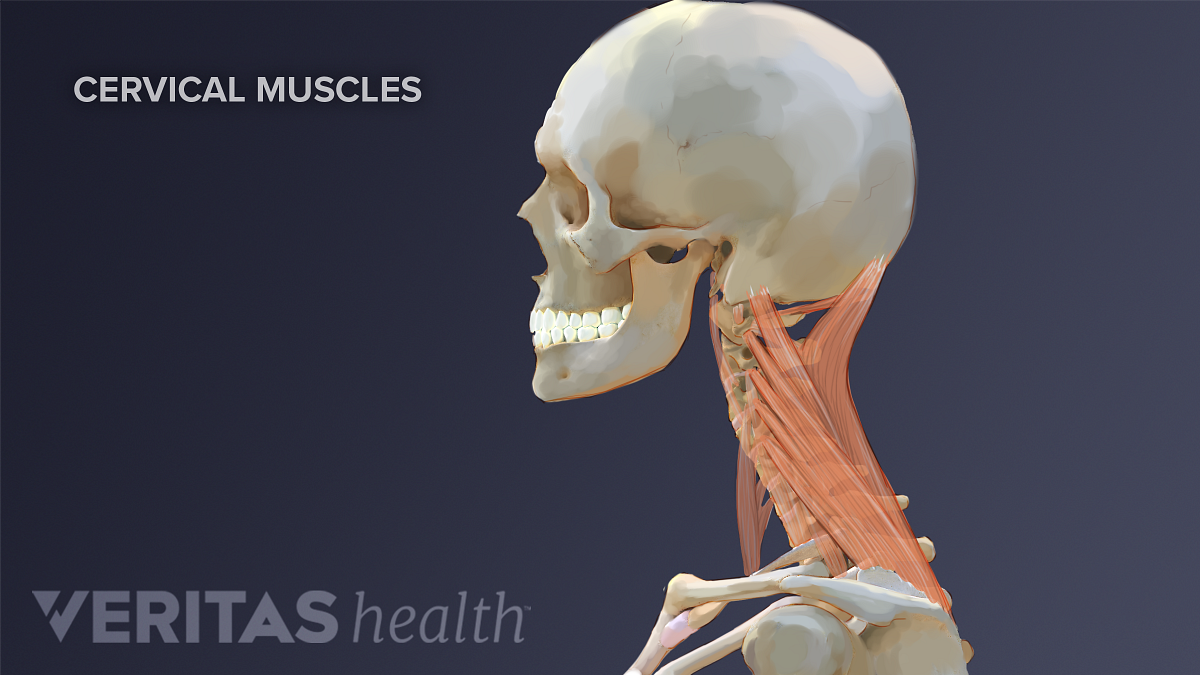



Neck Muscles And Other Soft Tissues
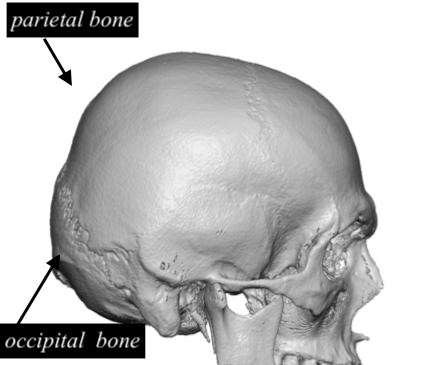



Flat Back Of Head Skull Anatomy Dr Barry Eppley Indianapolis Explore Plastic Surgery



Skull Anatomy Pictures And Information




The Skull Anatomy And Physiology
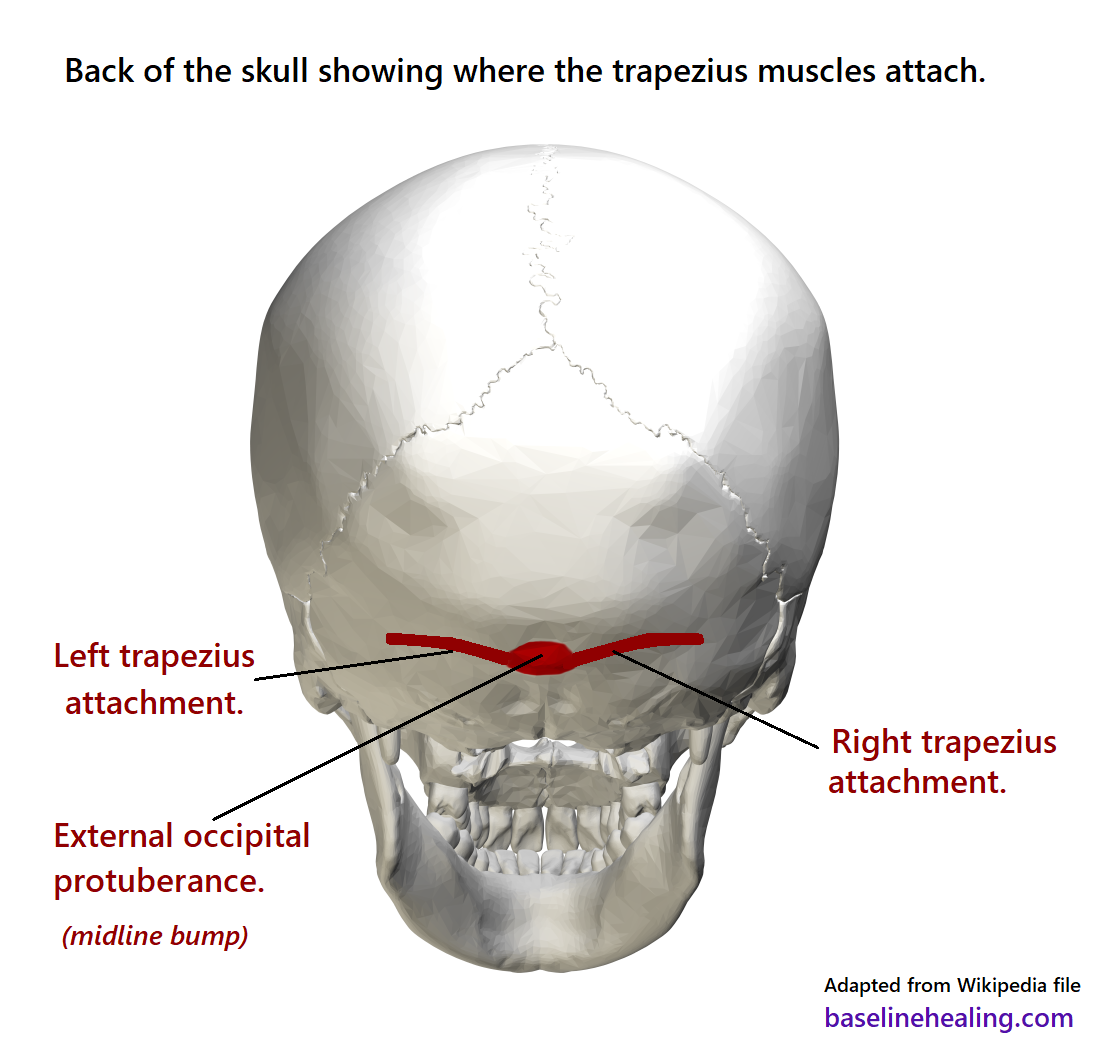



Upper Body To Base Line Connection The Trapezius Muscles




Skull Anatomy Images Stock Photos Vectors Shutterstock
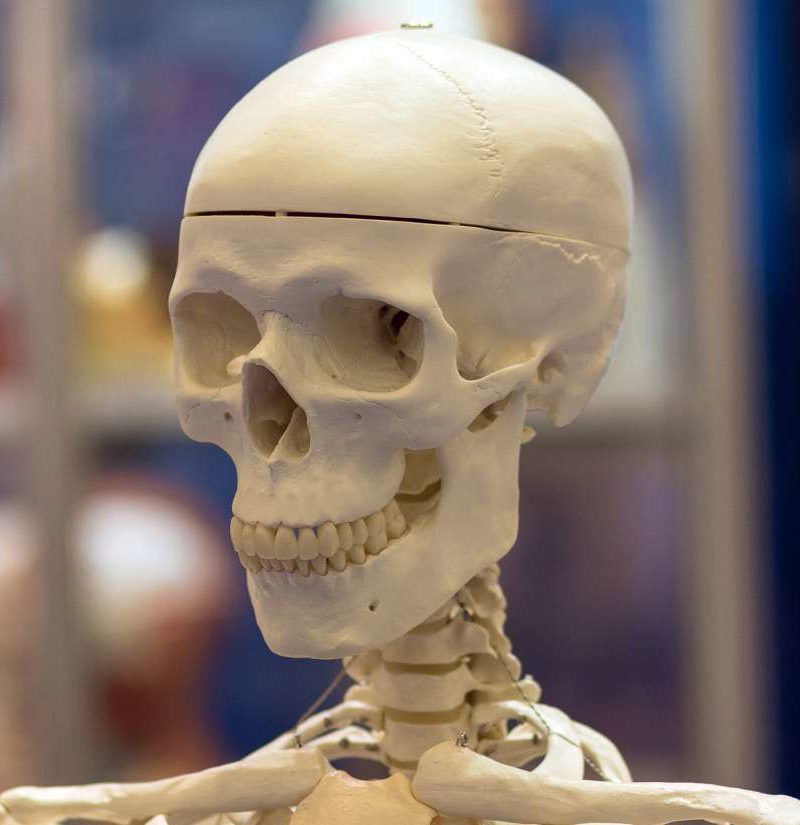




Temporal Bone Anatomical Diagram Function And Injuries




The Skull Anatomy And Physiology I




Anatomy Of Back Of Head Anatomy Drawing Diagram




Human Skull With Veins And Arteries Rear View Vascular System Of The Human Head Viewed From The Back Computer 3d Rendering Canstock
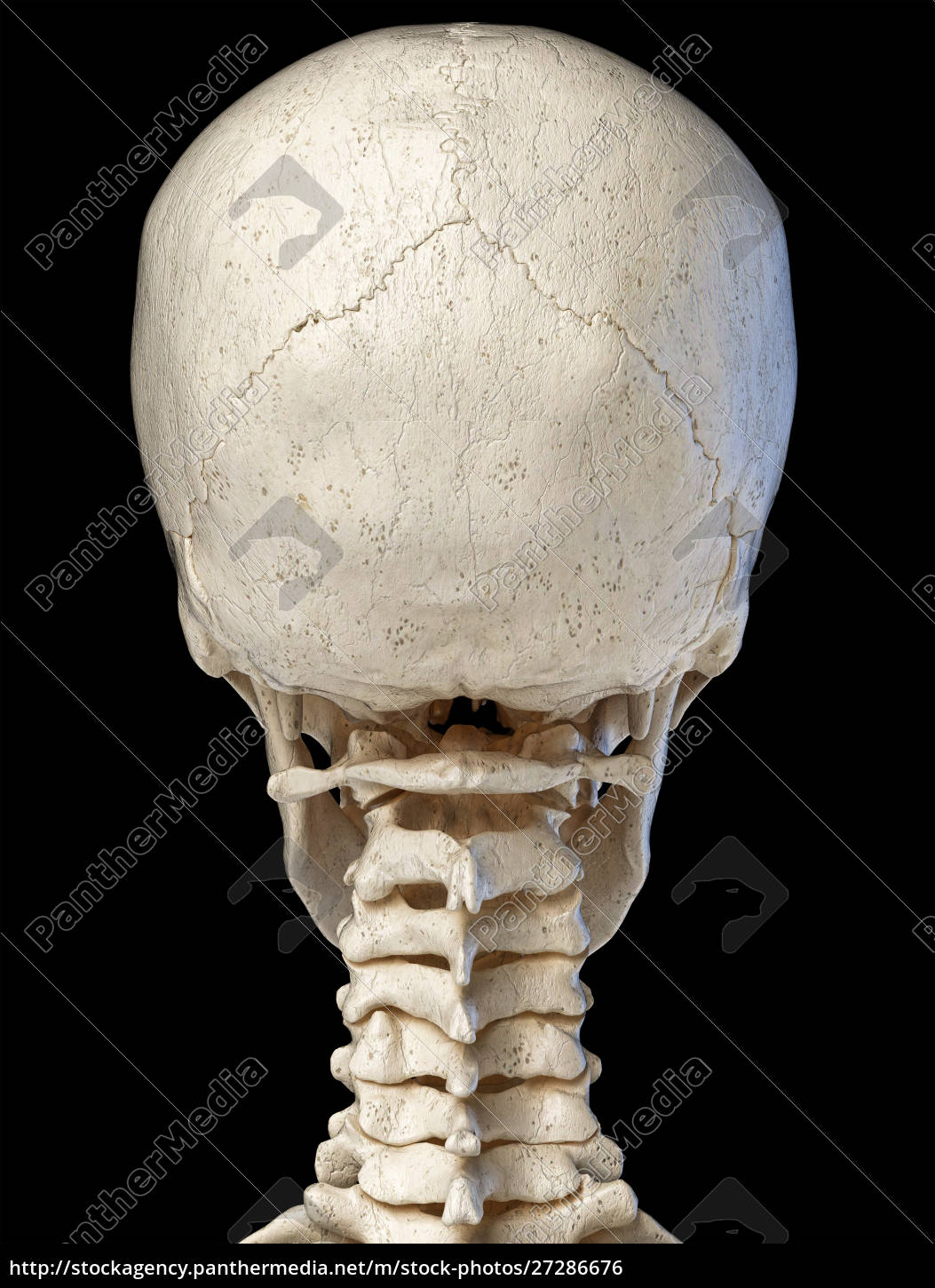



Human Skull Viewed From The Back Royalty Free Photo Panthermedia Stock Agency
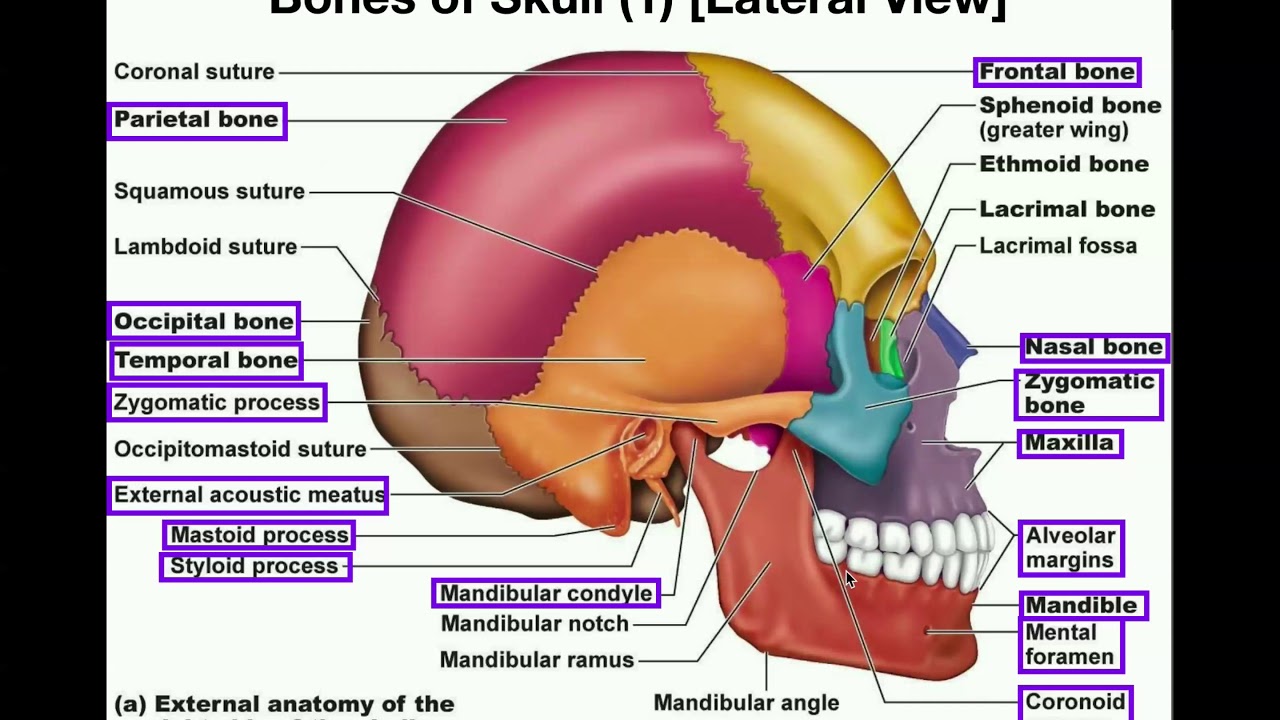



Anatomy The Human Skull Youtube
:background_color(FFFFFF):format(jpeg)/images/library/10686/Posterior_view_of_the_skull.jpg)



Skull Anatomy Structure Bones Quizzes Kenhub




Occipital Bone The Definitive Guide Biology Dictionary



Spinal Anatomy And Back Pain
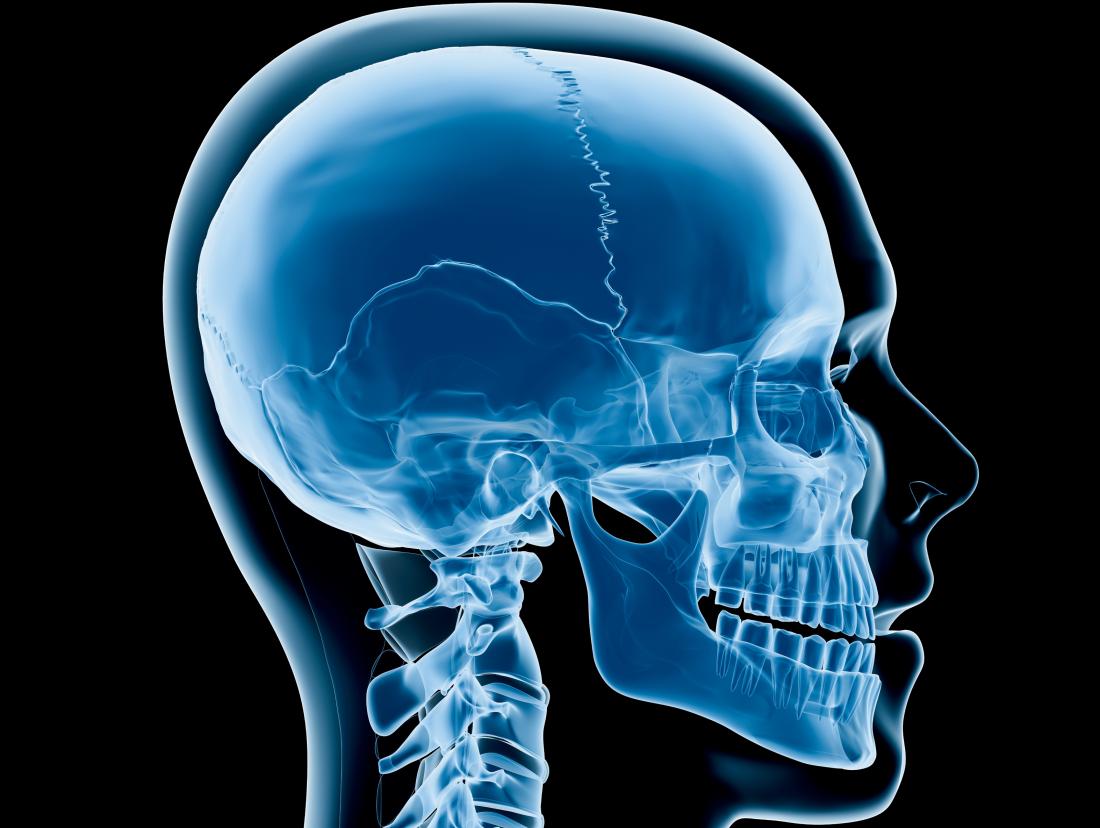



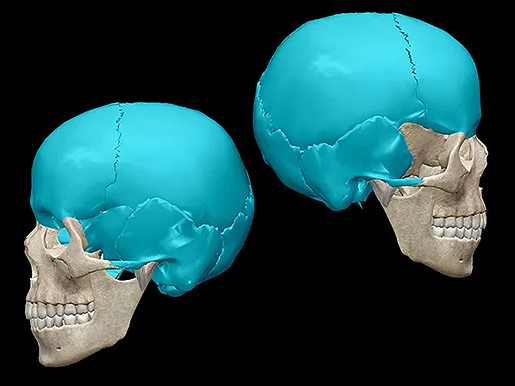
Craniosynostosis Types Causes Diagnosis And Treatment



Bones Of The Skull Learn In 4 Minutes Youtube




Bones Of The Head Atlas Of Anatomy
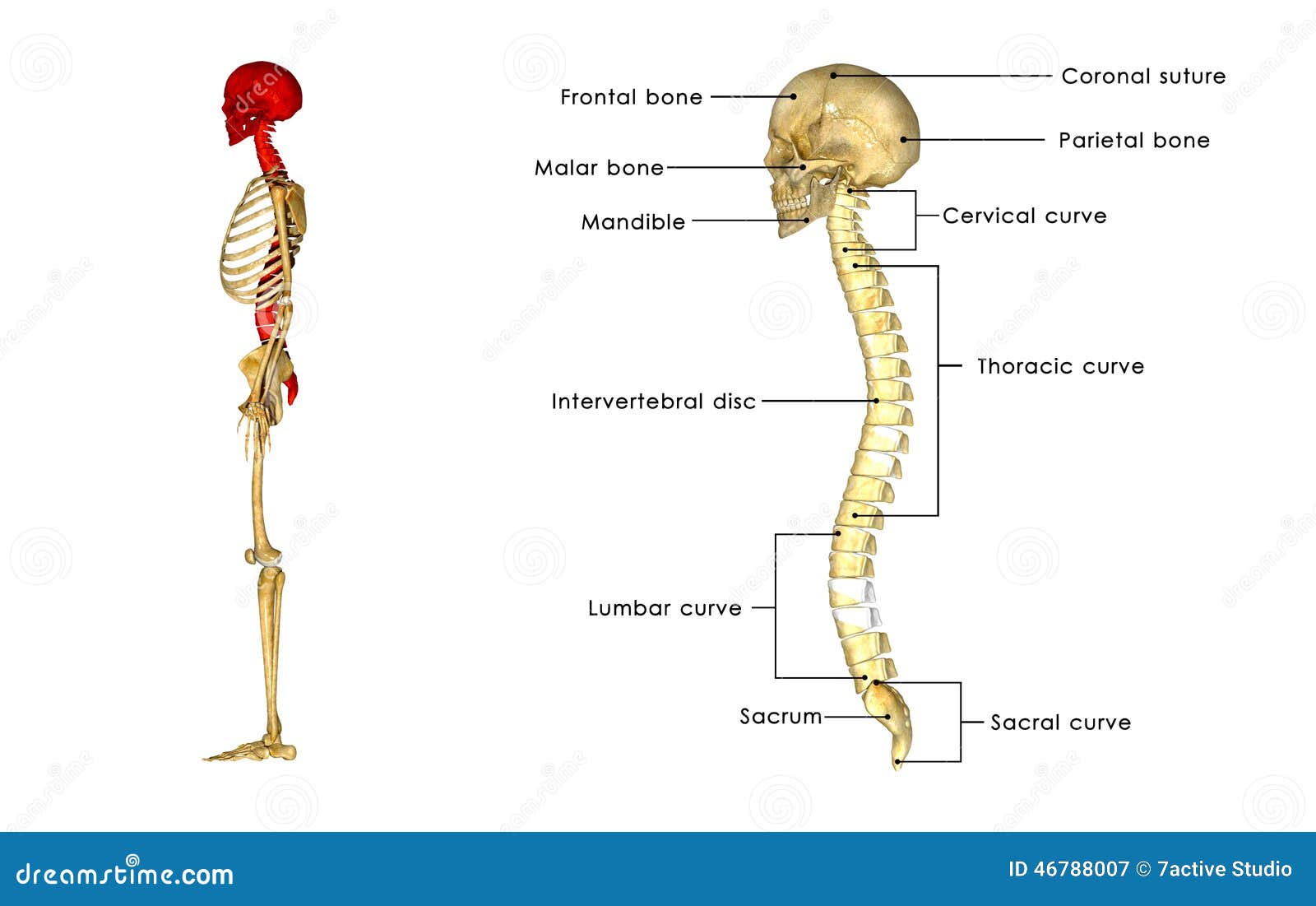



Back Bone With Skull Side View Stock Illustration Illustration Of Head Gland
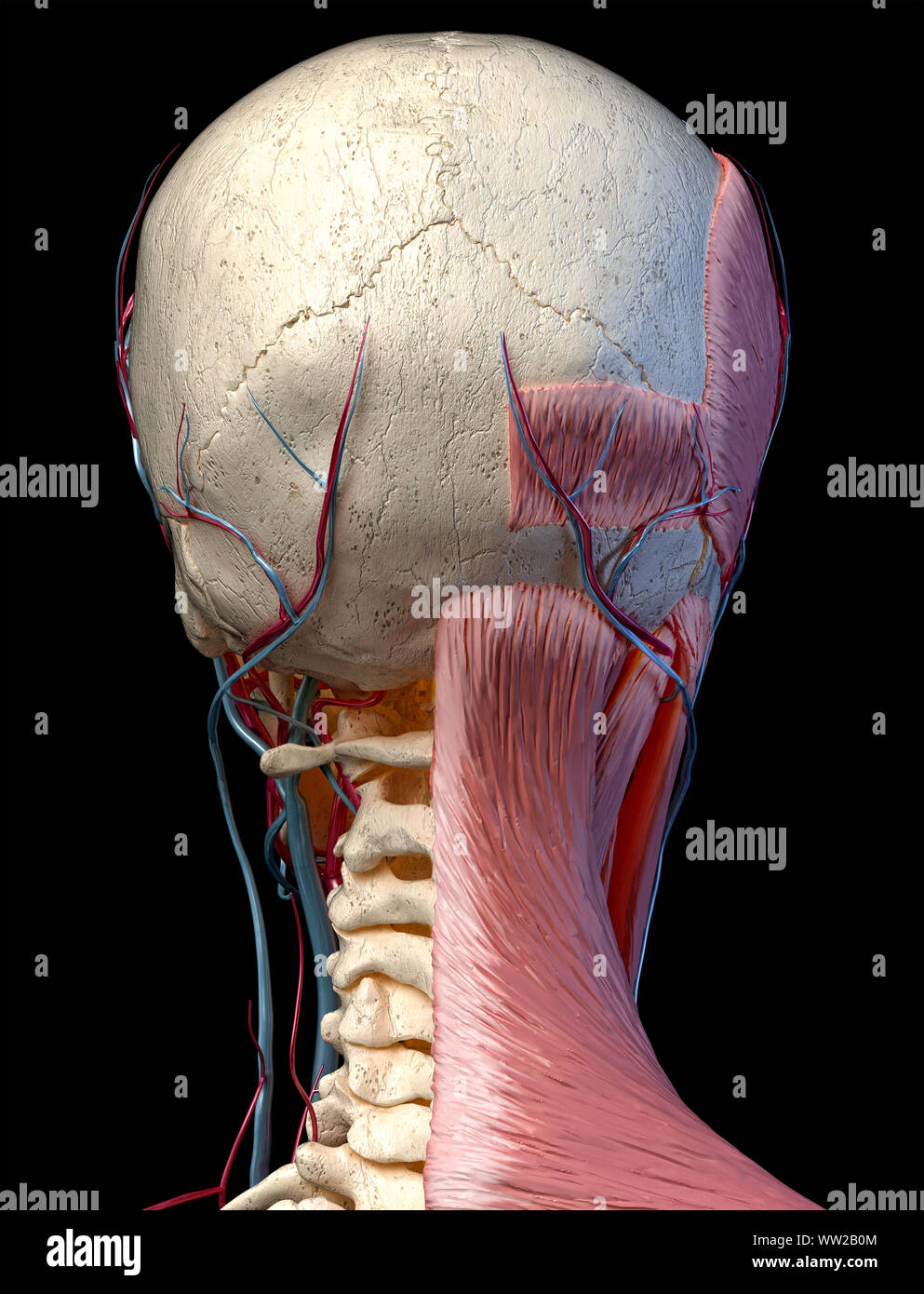



Human Anatomy 3d Illustration Of Head With Skull Blood Vessels And Muscles On Black Background Rear View Stock Photo Alamy




Skull Wikipedia
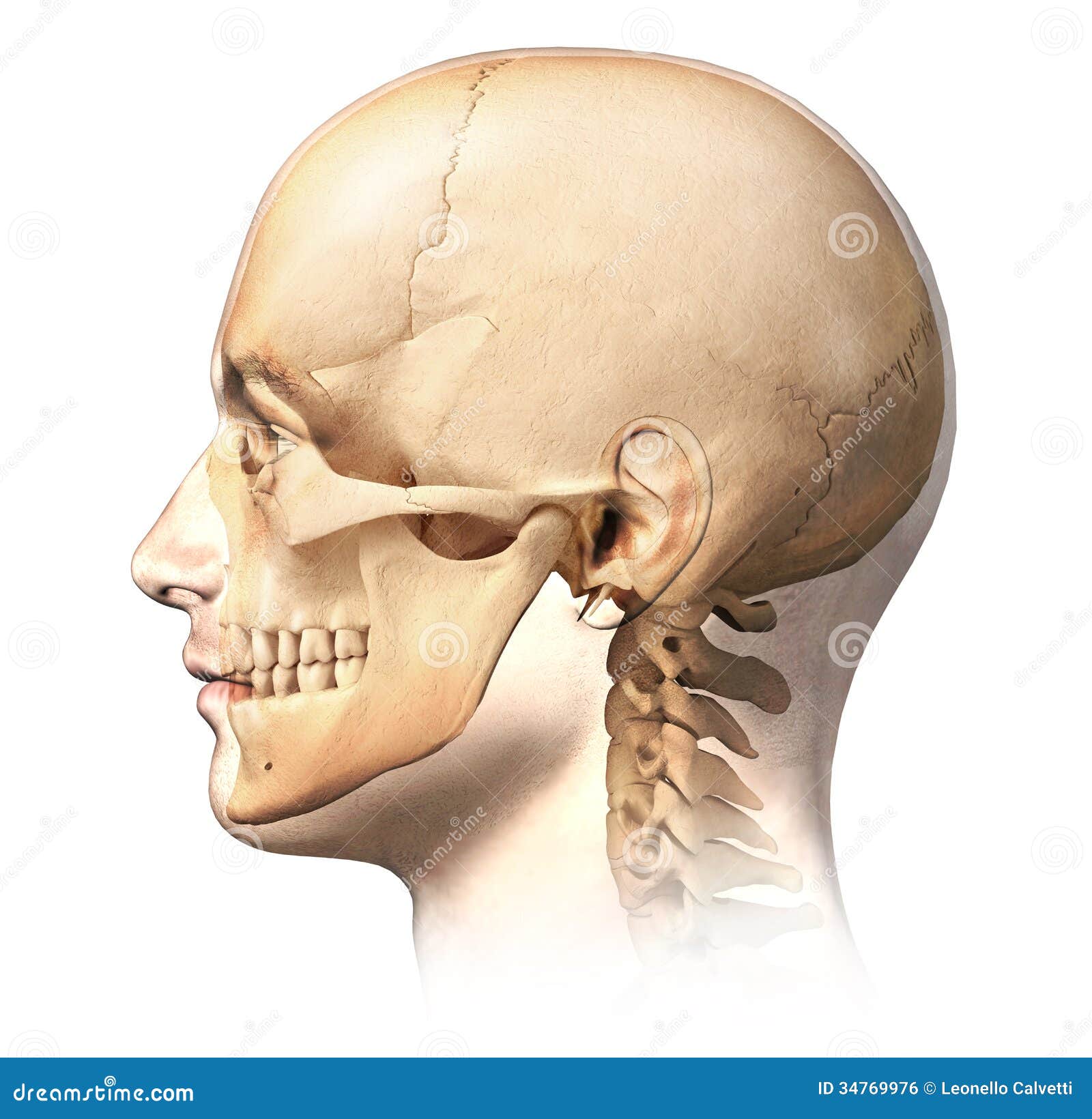



Male Human Head With Skull In Ghost Effect Side View Stock Illustration Illustration Of Inside Human
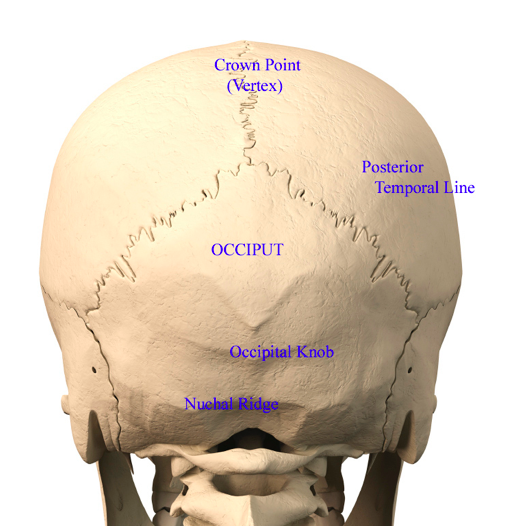



Back Of Head Skull Anatomy Dr Barry Eppley Indianapolis Explore Plastic Surgery



1




7 99 Aud 06 Anterior And Posterior Views Of Skull Anatomy Map 14 X25 Poster Ebay Collectibles Skull Anatomy Anatomy Bones Human Skull Anatomy
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/human-skull-with-veins-and-arteries--rear-view--1174640349-490cb7f8593945c4b1690b152e6a4074.jpg)



Occipital Artery Anatomy Function And Significance




Human Body Skull Anatomy External Occipital Protuberance Human Back Of Skull Face Human Png Pngegg




Cervical Dysfunction And Pain In The Head And Neck Causes And Osteopathic Options




Skull Scalp And Superficial Face
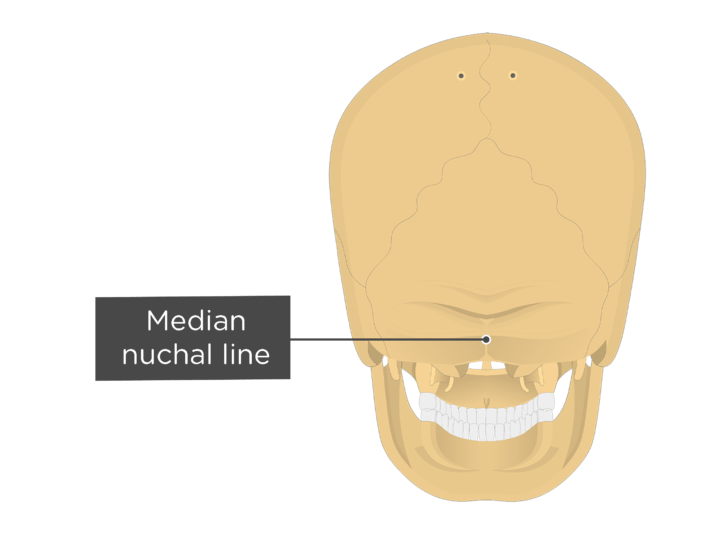



Occipital Bone Anatomy




Skull Back View The Human Skull Is A Bony Structure The Head In The Skeleton Which Supports The Structures Of The Face And Canstock




Skull Back Images Stock Photos Vectors Shutterstock




Skull Back Images Stock Photos Vectors Shutterstock




Skull Wikipedia



1
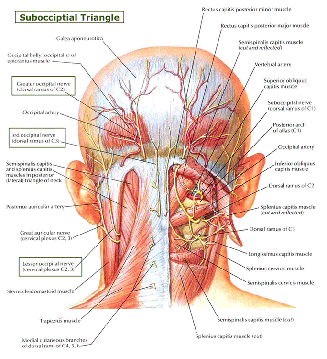



Occipital Nerve Blocks Complete Spine And Pain Care



Posterior And Lateral Views Of The Skull Anatomy Kenhub




Upper Cervical Spine Disorders Anatomy Of The Head And Upper Neck



Neck Bone Sticking Out
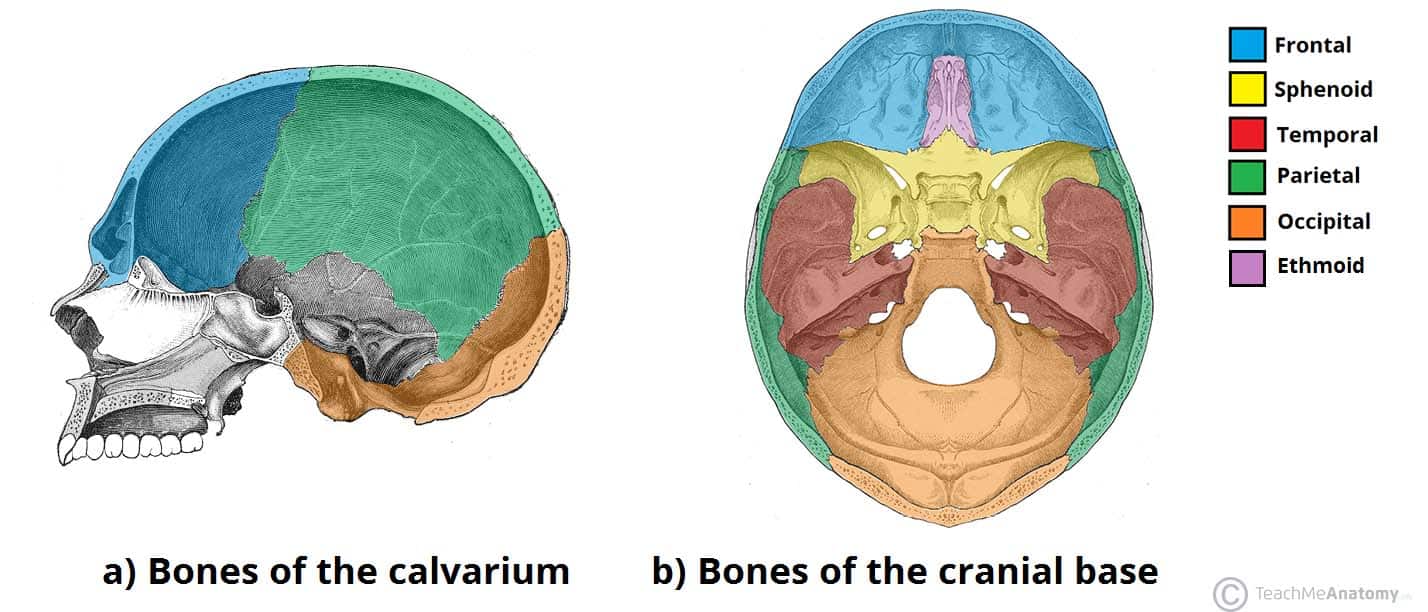



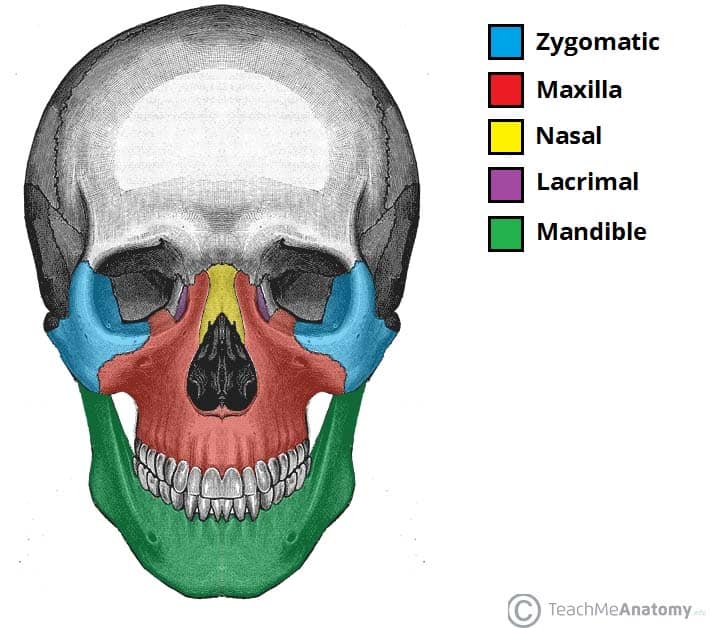
Bones Of The Skull Structure Fractures Teachmeanatomy



Bones Of The Skull Skull Osteology Anatomy Geeky Medics




Very Detailed And Scientifically Correct Human Skull Back View On White Background Anatomy Image Stock Photo Picture And Royalty Free Image Image
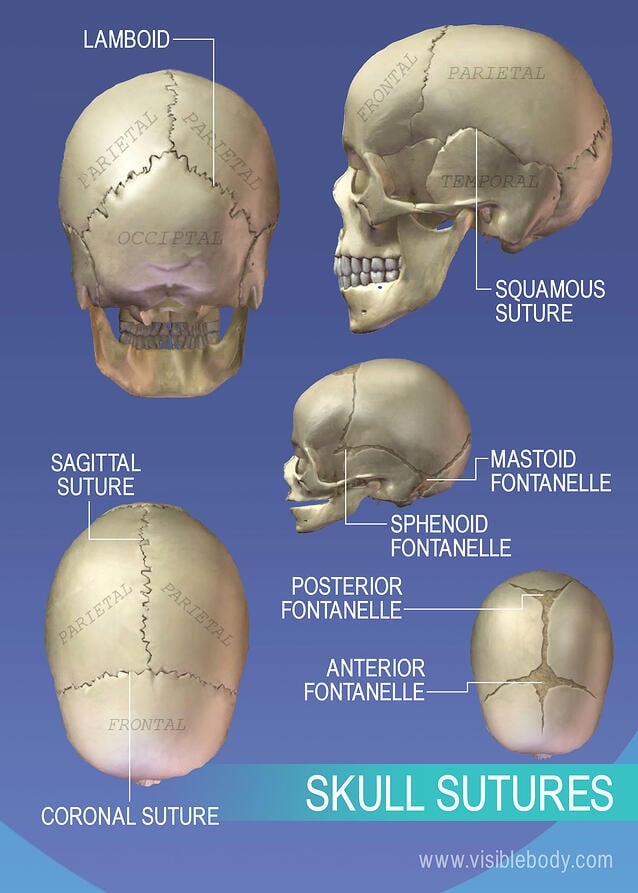



Axial Skeleton Learn Skeleton Anatomy




Skull Anatomy Terminology Dr Barry L Eppley



External Occipital Crest Canvas Prints Fine Art America
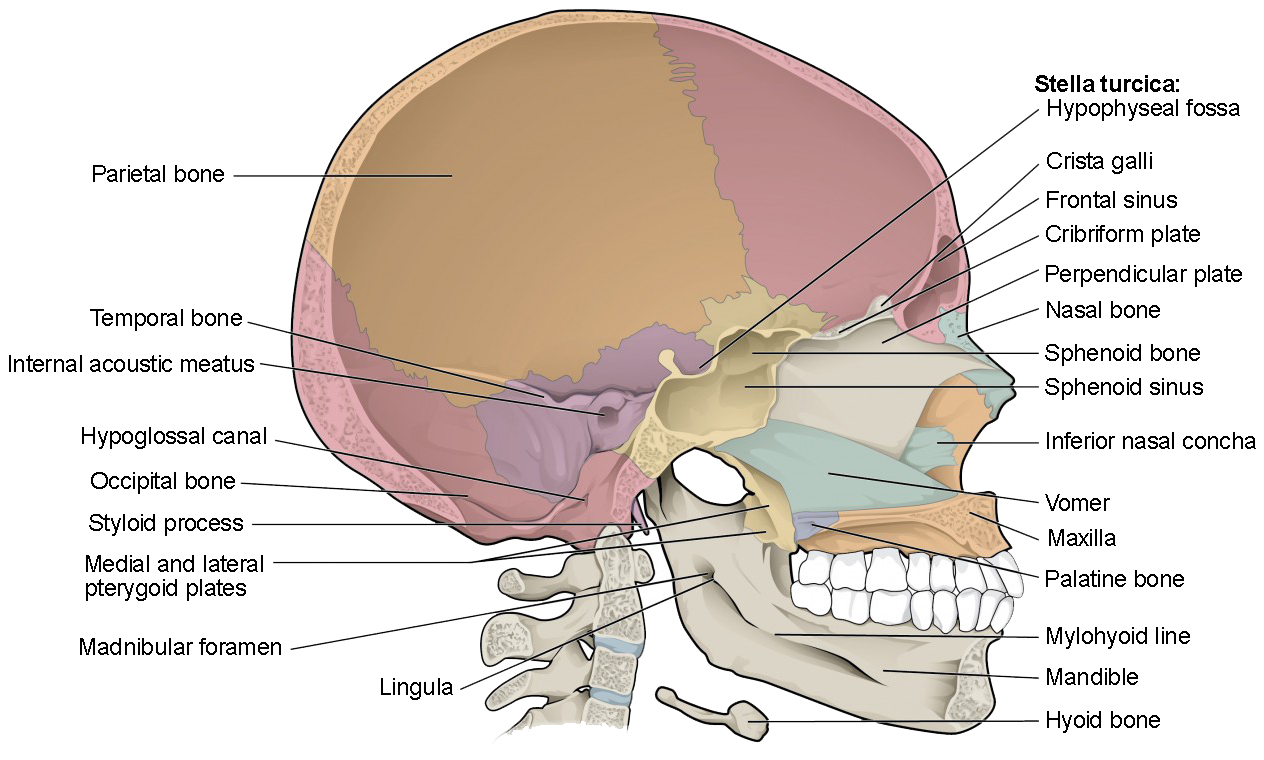



The Skull Anatomy And Physiology I



Poor Posture Due To Smartphone Use Leads To Horn Bone Growth In Skull Youtube




Crown Of Head Conditions Injuries And More




Human Head Neck Skull Anatomy Medical Anatomical Chart Educationalmodel Com Amazon Com Books



Cervicogenic Headache Causes And Risk Factors
:background_color(FFFFFF):format(jpeg)/images/article/en/posterior-and-lateral-views-of-the-skull/U0Gu2npm5ZRSP1eZgc4Jbw_Posterior_view_of_skull.png)



Posterior And Lateral Views Of The Skull Anatomy Kenhub




Back View Of Human Skeleton Of Head Stock Photo Picture And Royalty Free Image Image




Sagittal Skull Surgery For Peaked Head Shape Dr Eppley




No Teens Aren T Growing Skull Horns Because Of Cellphones Time




Lateral View Of Human Skull Anatomy By Alayna Guza Human Skull Anatomy Skull Anatomy Head Anatomy




Bumps Ridges And Soft Spots On A Baby S Head When Should You Worry Quest For Health Kc




Upper Cervical Spine Disorders Anatomy Of The Head And Upper Neck



Bones Of The Skull Structure Fractures Teachmeanatomy
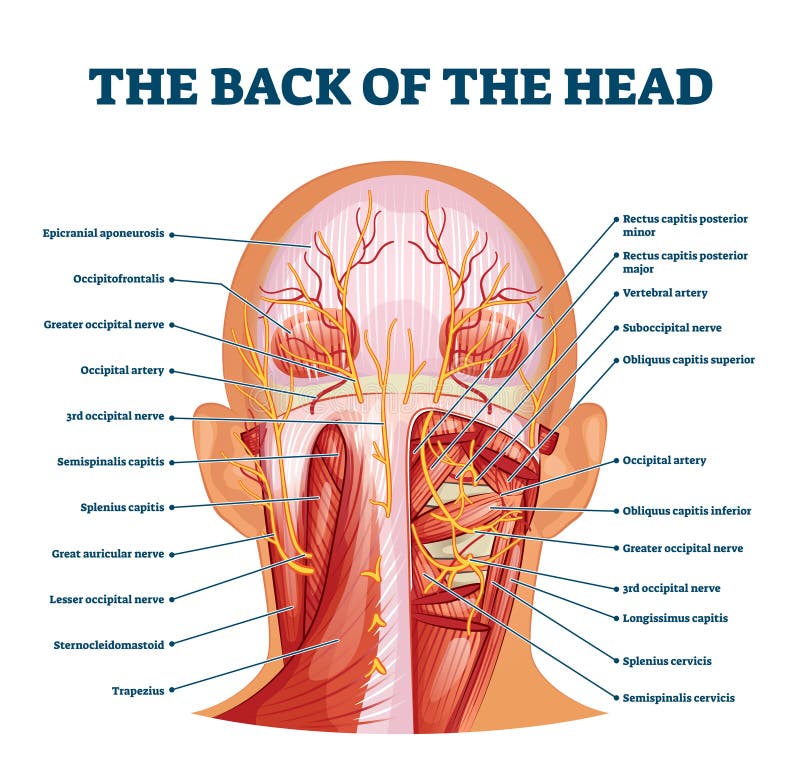



Back Of The Head Muscle Structure And Nerve System Diagram Stock Vector Illustration Of Labeled Muscle




7 3 The Skull Anatomy Physiology




Neck Anatomy Britannica
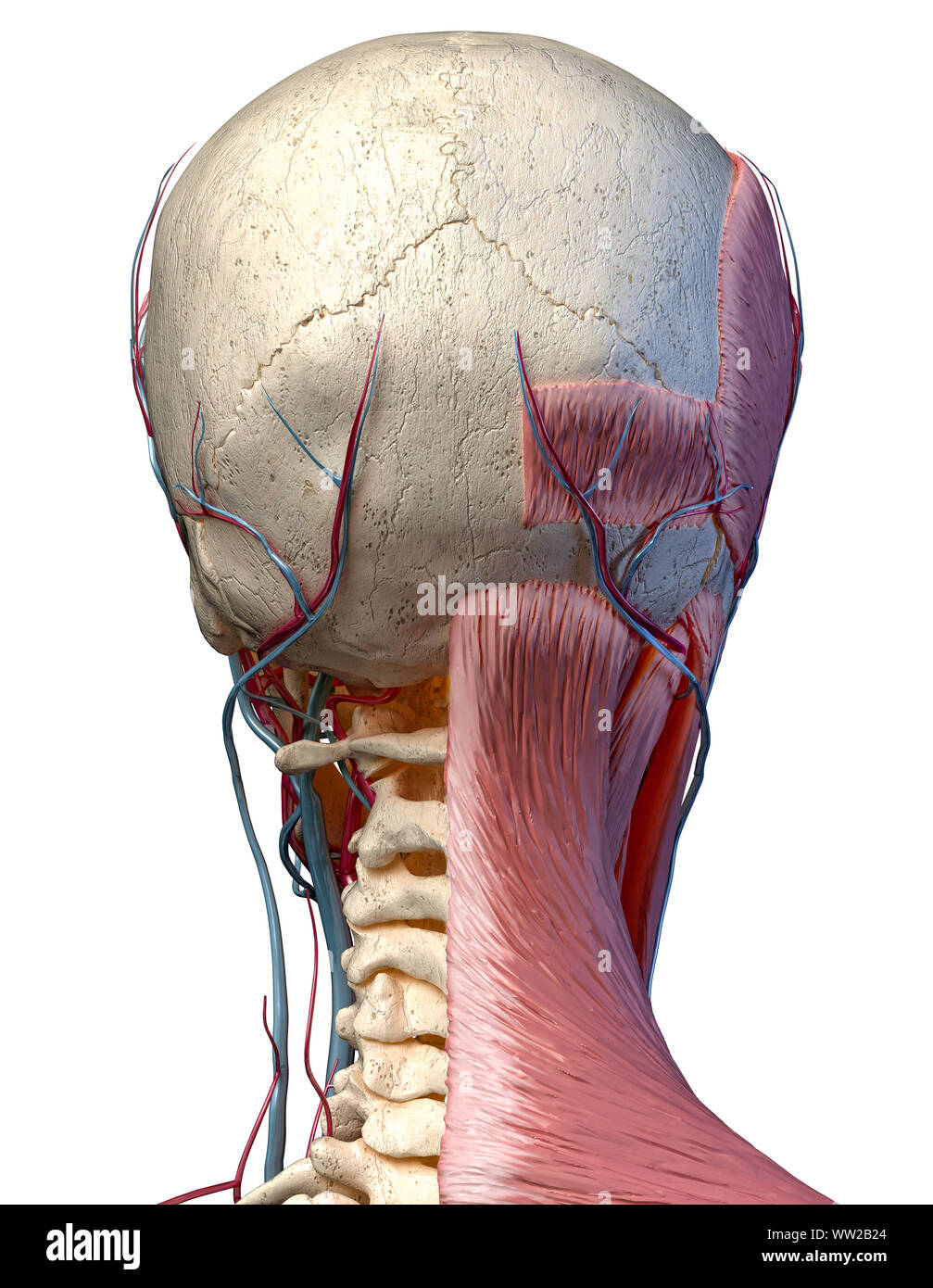



Human Anatomy 3d Illustration Of Head With Skull Blood Vessels And Muscles On White Background Rear View Stock Photo Alamy
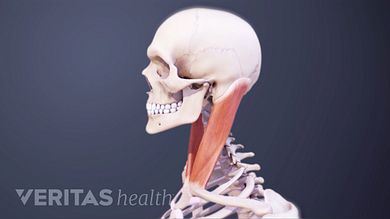



Neck Muscles And Other Soft Tissues
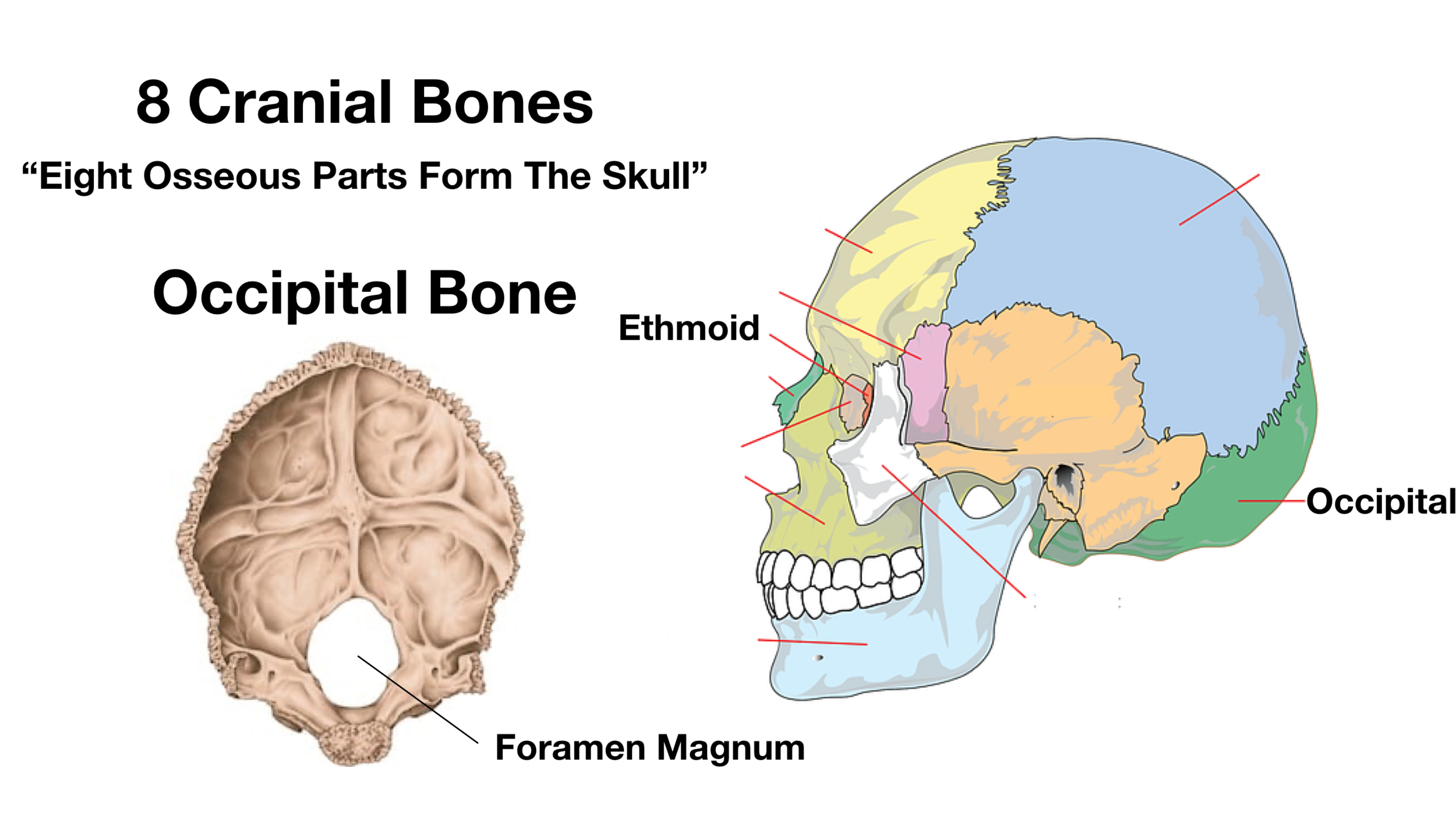



Skull Anatomy Cranial Bone And Suture Labeled Diagram Names Mnemonic Ezmed
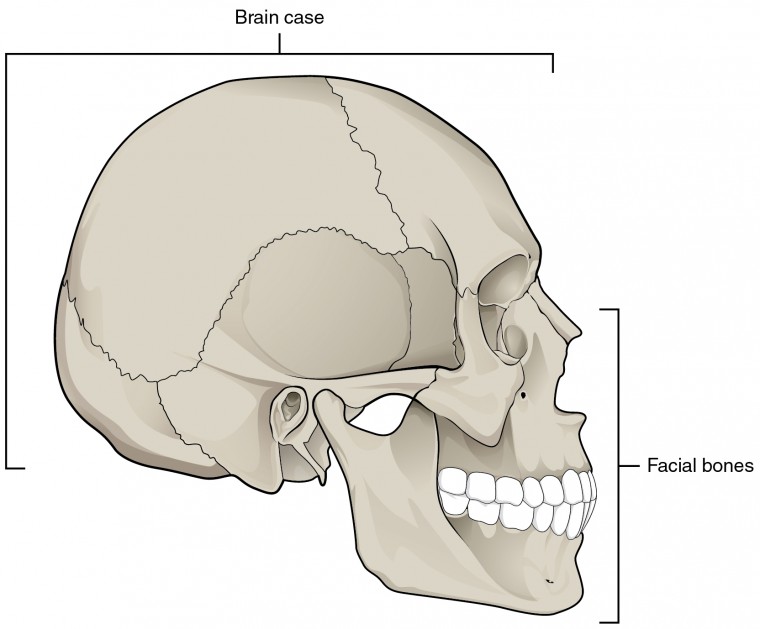



The Skull Anatomy And Physiology I




12 Types Of Bump On The Back Of The Head




Human Skull 3 4 Back View Skull Reference Human Skull Skull Anatomy




Human Skull Back View Canvas Print Barewalls Posters Prints Bwc




The Skull Boundless Anatomy And Physiology




7 3 The Skull Anatomy Physiology




Skull Anatomy Terminology Dr Barry L Eppley




Skull Definition Anatomy Function Britannica




Occipital Images Stock Photos Vectors Shutterstock



The Skull Boundless Anatomy And Physiology



Cranial Skeleton From The Back Anatomical Illustration Stock Photo Alamy



Cranial Bones Function And Anatomy Diagram Conditions Health Tips



Five Fast Facts About Skull Anatomy



0 件のコメント:
コメントを投稿